Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices designed to convert sunlight into electricity. They are made up of multiple solar cells, typically made from semiconductor materials like silicon. When sunlight hits these cells, the photons from the sunlight knock electrons loose from their atoms, generating a flow of electricity. This electricity can then be used to power various electrical appliances, homes, businesses, and even entire communities.
Solar panels come in various sizes and configurations to suit different applications. They can be installed on rooftops, in solar farms, or integrated into various products like solar chargers and solar-powered lights. The ability to generate electricity from the sun's energy makes solar panels a clean, renewable, and sustainable energy source, contributing to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change. As a result, solar panels play a crucial role in transitioning to a more eco-friendly and energy-efficient future.
Solar panels are a cornerstone of the renewable energy revolution and play a vital role in the ongoing global effort to transition to more sustainable and eco-friendly energy sources. These panels work on the principle of the photovoltaic effect, discovered back in 1839 by French physicist Alexandre Edmond Becquerel. The magic lies within the semiconductor material, typically silicon, which allows solar cells to harness sunlight and transform it into usable electricity.
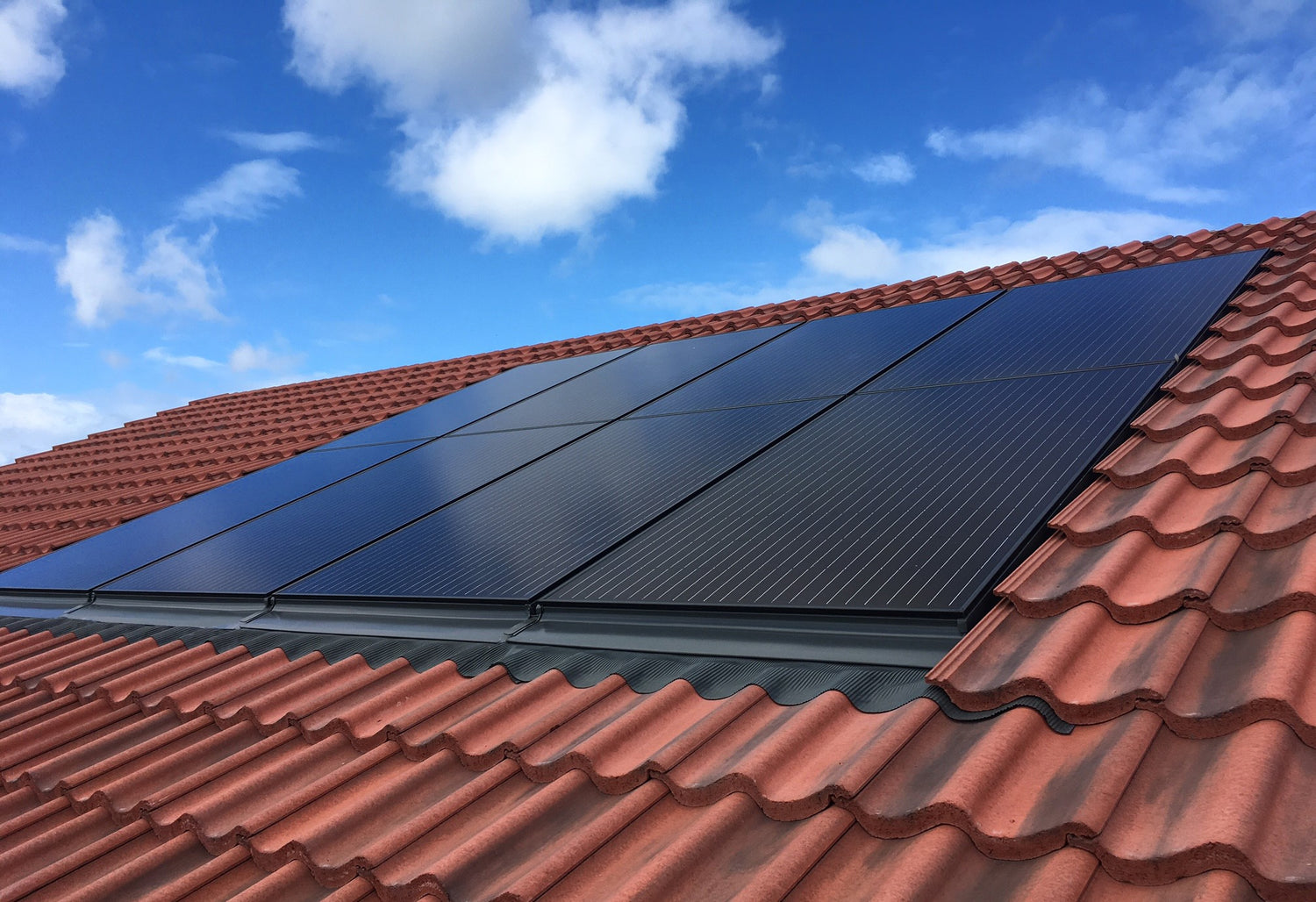
The structure of a solar panel is an intricate arrangement of several interconnected solar cells, each about the size of a compact disc. These individual cells are responsible for capturing the sun's rays and converting them into direct current (DC) electricity. The entire solar panel is then connected to an inverter, which converts the DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity, making it compatible with standard electrical systems.
Solar panels can be mounted in various configurations, with rooftop installations being one of the most common. By harnessing the abundant sunlight that falls on rooftops, homeowners and businesses can generate their electricity, reducing their dependence on conventional fossil fuel-based power grids. Additionally, solar farms or large-scale solar installations are deployed in sunny regions to generate massive amounts of clean energy, contributing significantly to the overall renewable energy capacity.
One of the most significant advantages of solar panels is their minimal environmental impact. Unlike traditional fossil fuel-based power plants, solar panels produce electricity without emitting harmful greenhouse gases, reducing carbon footprints and helping combat climate change. Furthermore, they require little maintenance and have a long lifespan, making them a cost-effective and reliable energy solution.
Governments and utilities around the world recognize the potential of solar energy and have introduced various incentives and subsidies to promote its adoption. These incentives often include tax credits, rebates, and net metering programs, allowing individuals and businesses to save money while embracing sustainable energy practices.